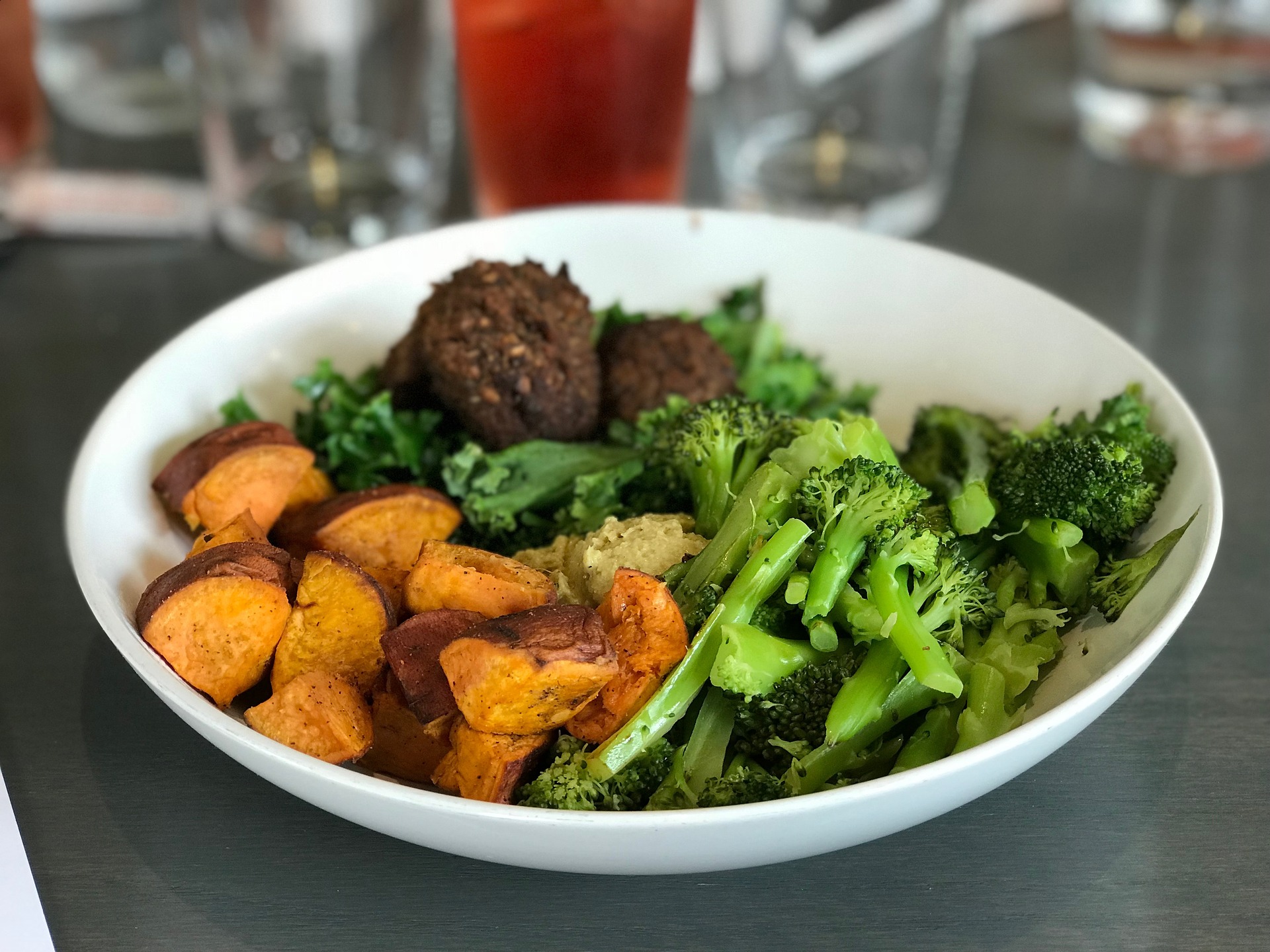Ask the lot out there what a Mediterranean diet is, and only a handful of them will give you a consistent answer. While many see it as one of the fad diets or a weight-loss program, it isn’t prescriptive – although the trend is picking up – like the Dukan or the Atkins diet. It is merely a pattern of healthy eating, and despite its name, the relationship with the diet and how people in Europe today live or eat is somehow less common.
The Mediterranean diet is banked on local farming, where people used to eat what they grew. The lifestyle has since declined with the increase and rise of processed foods and fad diets. The diet is deeply rooted in the culinary customs of the people from the Mediterranean region, especially Italy and Greece.
In fact, the United Nations (UN) documented the diet as endangered. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2013 distinguished Mediterranean diet as part of the intangible cultural heritage of the people in Italy, Greece, Portugal, Morocco, Croatia, Spain, and Cyprus.
You can follow the Mediterranean Diet on Noom. Give it a try to get your personalized eating plan today!
The Rise of the Relationship Between the Mediterranean Diet and Health
According to Mediterranean diet researchers, it wasn’t created in a laboratory. Antonia Trichopoulou, a professor at the University of Athens, says the diet has gradually evolved over five thousand years. He notes that the diet stemmed from the utilization of local resources to prepare food, and it was significantly influenced by factors such as religious views, the environment, and cultural practices.
Even before the documentation of the Mediterranean diet as a healthy way of eating, many people believed it was the best. This hints on the answer to the question, some people still ask, “Is the Mediterranean diet healthy?”
Trichopoulou defined it as a way of living. One that acknowledges and respects the people, where they live, and their religions. It focuses largely on local farm produce, cultural options, and seasoned foods.
The preliminary studies of the Mediterranean diet began with Ancel Keys. Unknown to him, more researchers would later carry out an in-depth analysis of the topic.
After the second world war, he carried out a legendary project; the Seven Countries Study that sought to establish health benefits of close to 13000 middle-aged men in the US, Japan, Italy, Greece, the Netherlands, Finland, and finally former Yugoslavia. The rise in the number of deaths related to heart disease in the US captured Ancel’s attention, and he wanted to find out why.
The results from the remarkable study found that subjects from Crete had reduced rates of cardiovascular diseases compared to the other subjects in the rest of the countries. The findings were associated with the men’s diet after the war that only consisted of beans, fish, grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Since the Seven Countries Study, hundreds of other studies seeking to establish more health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have been performed. A few of the positive impacts are an increased lifespan, weight loss and its maintenance, improved cognitive function, eye health, lower risks of certain diseases like cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and diabetes, reduced rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, as well as fertility. There are also studies linking the diet to decreased levels of oxidized low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol and blood pressure.
According to the Lyon Diet Heart Trial conducted in 1998, 56 percent of subjects put on a Mediterranean diet for three years showed a reduced risk of dying while those with reduced myocardial infarction ranged between 50 and 70 percent.
Consequently, 50 percent of the subjects in another study, the Gissi Prevenzione Trial performed in Italy featuring over 11,000 male and female individuals, showed a reduced mortality rate.
More studies regarding the Mediterranean diet benefits are ongoing. Recently, a publication was made that attracted attention across the globe. The PREDIMED trial done by Spanish researchers found that the incorporation of nuts in the diet lowered the risk of cardiovascular disease by 30 percent, and stroke by 49 percent assessed alongside the low-fat diet recommended by the American Heart Foundation.
Now, is the Mediterranean diet healthy? From history, the plan is apparently no magic bullet. It isn’t based on one food that delivers particular benefits, rather it is a form of healthy eating. The diet is made of plant-based, locally produced, and nutrient-dense foods. You can bring the benefits of the Mediterranean diet anywhere in the world. All it takes is to translate the key components of the diet into your lifestyle, and you are on your way to leading a healthy life.

The Difference Between Noom and Other Plans and Programs
When following the Mediterranean diet plan, it is helpful to have specifics of foods that should be avoided or moderated along with the types of foods that should be increased. Note these details of which foods to consume and not to consume below along with this convenient meal plan to follow.
When it comes to learning how to eat and how to live for weight loss, Noom works from a psychological perspective. According to the Chief of Psychology for Noom, Dr. Andreas Michaelides, “By understanding the past behaviors and attitudes of all types of users, we know the best way to meet our users where they are in their journey to help them maximize their change of long-term weight-loss success.” Noom, as a weight-loss platform, uses the power of food logging, among other advanced technologies, to teach simple, key behaviors for lasting change. Behavior changes that include self-efficacy, motivation, and knowledge are just the start of how psychology can interact with food, so you lose more weight in a way that lasts a lifetime.
Noom works with tech-based tools partnered with support from real-life coaches in a structured program that connects the user with the social support and positive reinforcement needed to change behavior in a way that increases the likelihood of success.
Not all dietary changes are for everyone, and no two weight-loss plans should be the same, which is precisely how Noom works.
By identifying specific areas where changes can be made to reach goals of weight loss and health improvement successfully, users realize where their best changes are to be made and how those changes are incorporated into a lifestyle they can adopt for the long-term.
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
Now that you have a glimpse of its historical background let’s get to the basics of the Mediterranean diet.
When people think about a Mediterranean diet, most of them picture a pasta, or pizza, or lamb satay from Greece. On the contrary, these foods hardly make the fundamental components of the diet. The Mediterranean diet is worth sacrificing and chasing after. You shouldn’t have to think twice about switching from pepperoni or pasta to consuming healthy fats and fish. The transition might take some getting used to, but once you are on track, you are on the way to a healthy, long life.
Traditionally, a Mediterranean diet is based on fruits, vegetables, seafood, nuts, dairy, olive oil, and maybe a glass of red wine. This was the typical lifestyle of the people of Greece, Southern Italy, and Crete back in the 1960s when they experienced fewer and less disease outbreak, and their lifespan was one of the highest amidst limited health care services.
Nevertheless, the actual Mediterranean diet is way more than just nutrient-dense or wholesome foods. It is all about sharing meals and incorporating daily physical activity. This is part of the Mediterranean diet pyramid, a model that ensures the food you eat positively influences your mood and brain function, apart from helping you foster a worthy appreciation for the gratifications of consuming nourishing and savory foods.
The diet is inexpensive, not to mention how you get to enjoy the perfect meal – one that is nutritionally balanced has the right texture, beautifully flavored, and full of color. The diet should, at all costs, never feel restrictive.
How Does the Mediterranean Diet Work?
There are so many differences between people in terms of the details of the Mediterranean diet. Even nutritionists and health professionals have varied views. Nonetheless, the principles are apparent, which is why how the diet works differs from one person to another. The emphasis is on eating fruits and lots of vegetables, legumes, nuts, using olive oil, spices, and flavorful herbs, some seafood several times a week, eggs, yogurt, and cheese, with moderation, while sparing red meat and sweets for only a few occasions.
If necessary, you can top it off with a glass of red wine, and above all, always stay active. Do lots of exercise and other activities you are capable of.
Remember, the Mediterranean diet is more of a lifestyle, not a structured diet. Being an eating pattern it is up to you to determine the number of calories you consume daily. This means that if you are using the Mediterranean diet to lose weight, you should carefully balance your calories to lose or sustain a healthy weight. Shape your Mediterranean menu well for the best results.

Mediterranean Diet for Weight Loss
So, does the Mediterranean diet for weight loss work? While others ask the question, some are concerned that the diet being relatively high in fats like avocado, olives, and olive oil, may keep them fat. Research, however, is proving that to be wrong.
The answer to the question, however, is that the Mediterranean eating style isn’t particularly a weight-loss diet plan, but if one limits the ingestion of red meats, unhealthy or animal fats, and junk foods, he or she may realize weight loss.
But again, it is highly dependent on the procedures or methods you adopt and how it relates to your current diet plan.
For example, if you go by the rule of following the calorie-deficit diet plans, that is, consuming fewer calories than the daily recommendation, it will allow you to shed some pounds. You can also burn the extra calories through exercise.
Nevertheless, there is evidence that the Mediterranean diet can be used to address weight loss. One such study was published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology journal in 2016. The study analyzed the PREDIMED study, and it was discovered that subjects on the Mediterranean meal plan lost a negligible size on their waistlines. Those who supplemented the Mediterranean diet with olive oil lost the most weight.
Mediterranean Diet Benefits
Mediterranean diet comes with lots of health benefits. It isn’t cited as being the healthiest diet without reason, and the lower death rates in regions where the diet is highly predominant is a testimony to its greatness.
Some experts, on the other hand, believe that the health benefits of the diet aren’t only associated with the dietary factors. The physical activity, reducing the amounts of consumed alcohol, cessation of smoking, and or the lower Body Mass Index (BMI) are other fundamental reasons for the advantages.
The diet is said to affect the risk factors for cardiovascular disease positively. But compared to other diets, the difference isn’t that big. One meta-analysis that was done in 2003 compared vegan, Mediterranean, high-protein diet, low-carbohydrate diet, high-fiber, vegetarian, and low-glycemic diet with control diets. From the findings, it was concluded that the low-carb, high-protein, Mediterranean, and low-glycemic diets are efficient regarding the improvement of the markers of the risk factors for both cardiovascular disease and diabetes. The results showed limited proof of the effect of the vegan diet on lipid levels and glycemic control unassociated with weight loss.
Despite the various concerns raised about the quality of the systematic reviews as well as the meta-analyses used to determine the effect of the Mediterranean diet on the symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, newer reviews have also arrived at similar findings. They conclude that the diet does indeed improve risk factors such as high blood pressure.
The diet is credited for being high in monounsaturated fats together with dietary fiber but low on saturated fats. The health benefits are believed to be because of the olive oil, which contains unsaturated fats, especially oleic acid, whose clinical research on its significance to health is still ongoing. A study published in 2014 made a conclusion that an increase in the consumption of olive oil is linked to a lowered risk of all-cause death, stroke, and other related problems. On the other hand, the monounsaturated fatty acids from both animal and plant sources depicted zero significant effects.
Be that as it may, here is a detailed view of more Mediterranean diet benefits.
Just like the Mediterranean Diet works to help users adopt healthier eating habits, so does Noom – a tech-based psychological program designed to treat each users like an individual whether eating Mediterranean or other plan.

Reduces the Intake of Sugars and Processed Foods
The composition of the diet, vegetables, fruits, some legumes, and nuts, looks much like a low-carb diet that cuts on the intake of sugary foods and processed foods. Compared to an ordinary US diet, the Mediterranean meal plan is free of artificial ingredients, preservatives, or GMO, and is low on sugars.
People in the Mediterranean region eat fruits in place of something sweet. Alternatively, they may opt for small amounts of desserts made with honey.
Far from the eating of plant-based whole foods, seafood or fish is another great source of Mediterranean nutrients along with cheese from cows, sheep, or goats – in moderation – and yogurts for the contribution of healthy fats and cholesterol. What makes the central part of the diet include fish like sardines or anchovies.
Encourages Healthy Weight Loss
Sticking to the Mediterranean diet plan may just be the secret to the healthiest way of losing and sustaining weight. The beauty of it is that you won’t have to go hungry to lose weight. It is worthwhile and helps ensure that your body weight is manageable. It naturally reduces the intake of fats simply through the eating of sufficient nutrient-dense meals.
There is sufficient room for one to have optional plans. If you would rather go with a low carbohydrate diet or the low-protein meal plan, or whatever fits somewhere in between, you are always at liberty to choose what will deliver the best results.
Apart from improving the quality of nourishing fats, it also keeps the carbs low and enhances the ingestion of better-quality protein foods. With the high amount of seafood at your disposal, you may choose to lose weight in a no-stress kind of way. You can top this up with high-quality dairy products for probiotics.
One of the main reasons why this diet works for weight loss is because it is easy to follow and isn’t restrictive compared to other types of diets. You still get to eat most of your favorite foods.
Nevertheless, following the diet for at least six months is recommended for weight loss to be realized. The exercise also comes in handy, and it speeds up the process of burning fat. All you have to do is limit the intake of the foods that may sabotage your goals.
There are numerous studies supporting weight loss through the adoption of the Mediterranean meal plan. In 2008, the New England Journal of Medicine published a study that focused on 322 individuals with obesity who were put on a calorie-restricted Mediterranean diet, a calorie-restricted low-fat diet, or unrestricted low-carb diet. The results were as illustrated below:
The Mediterranean group lost more weight than the low-fat group. Although the low-carb diet group lost more weight, it was only by a negligible amount. The unrestricted low-carbohydrate diet subjects lost 10.3 pounds, whereas the Mediterranean group lost 9.7 pounds. Also, the Mediterranean diet subjects realized an improvement in blood sugar and insulin levels.
It was, therefore, concluded that the Mediterranean diet could be highly effective for shedding some pounds as well as improving the symptoms of diabetes in comparison to a low-fat diet.
Improves Heart Health
The heart health benefits of the Mediterranean diet were long-established by Ancel Keys in the 1950s. It was not until the 1990s that the diet became popular in the United States.
According to the results of his Seven Countries Study, experts claim the benefits are partly due to an active lifestyle, prohibition of too much eating of red meat and sugars, all of which are associated with little to no occurrences of coronary heart disease or stroke. The monounsaturated fat and the focus on fruits and veggies are responsible, share the research.
The adherence to this type of diet is also associated with low mortality rates caused by cardiovascular diseases. Olive oil contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) in plenty. The remarkable protective effect offered by the oil has been demonstrated through numerous studies, which conclude that the Mediterranean diet plan lowers the rate of cardiac deaths by 30 percent and sudden cardiac arrest deaths by 45 percent.
Another study that showed a comparison of high blood pressure in individuals consuming lots of sunflower oil and those with an increased intake of extra-virgin olive oil showed that the latter indicated a decreased blood pressure by substantial amounts.
Olive oil also makes nitric oxide more bioavailable, and this is significant in the lowering of hypertension. The effect is that the arteries are kept free from vasoconstriction, which maintains the optimal blood pressure. Moreover, it also improves the endothelial function while at the same time preventing the body from the harmful consequences of oxidation.
Helps Fight Cancer
There is a chance of a six-percent decreased risk of dying from cancer if one follows a Mediterranean diet strictly, some studies suggest.
This also aligns itself with another meta-analysis that resolved that the diet causes a decreased rate of cancer.
There is also evidence that suggests how following the diet reduces the number of deaths resulting from cancer, and how the consumption of oil is indeed ideal in the lowering of the development of cancer.
The principles at which cancer prevention occurs when an individual is on the diet is owed to the fact that it encourages a balanced ratio of the essential fatty acids and the elevated amounts of dietary fiber, the polyphenols, as well as the antioxidants contained in the Mediterranean food list.
This diet plan helps in the fight against cancer in almost every aspect. It is antioxidant-rich, prevents DNA damage, inhibits cell mutation, fights inflammation, and delays the potential growth of tumors. It is also a common belief that olive oil is beneficial in the treatment of cancer and the potential of the development of stomach or colon cancers, all thanks to reduced oxidative stress, sustaining a healthy weight, and its tendency to enhance optimum levels of blood sugar.
With Noom you can track your blood sugar to see how foods affect levels.

Helps in the Prevention or the Treatment Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes who follow the diet stand a better chance in terms of the prevention of the disease and the improvement of glycemic control. Some studies have been performed to determine the claim.
Two studies carried out in 2014 uncovered that the Mediterranean diet is linked with a lowered chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
Also, other studies show that those following the diet experience lower fasting glucose levels than those who do not. Consequently, if you compare the dietary guidelines for people with diabetes as per the American Diabetes Association (ADA) with the Mediterranean style of eating, they are very similar.
Evidence from another study proves that the Mediterranean diet functions as an anti-inflammatory meal plan that could be useful in fighting illnesses related to chronic inflammation, including type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
The balance of whole foods and the regulation of blood sugar levels allows the body to burn more fats efficiently, keeping one energized throughout the day. Usually, what makes part of a natural diet for the diabetic is a low-sugar diet with fresh produce and healthy fats.
The American Heart Association agrees that the Mediterranean diet contains more healthy fats than the standard diet, which is higher in poor-quality fats.
The balance ensures that the body remains in hormonal homeostasis, which means insulin levels are minimized. As such, the ratio is perfect for making sure that body weight and hunger is under control. Nonetheless, the effectual result is that a person’s mood remains in check; he or she will remain calm, energized, and relaxed, not to mention how easy it will be to exercise.
The only source of sugar in the diet is from fruits and natural sweeteners such as honey, and perhaps from wine or the home-made Mediterranean dessert. Plenty of water, some coffee, and wine in moderation make part of the diet. Keeping all these factors in check, and exercising ensures that the levels of blood sugar don’t become elevated, which is the reason behind rare instances of insulin resistance.
Improves the Cognitive Function
Mediterranean diet is a step in the right direction regarding the natural ways of preserving memory and fighting diseases like Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s and treating dementia. These cognitive disorders arise because the brain doesn’t get enough amounts of dopamine, which helps in the regulation of mood, body movements, and sound thought processing.
A Mediterranean-style cooked meal or salads with olive oil or nuts, anti-inflammatory vegetables, and fruits has been proven to fight the decline of cognitive function related to aging. Thus, following the diet keeps the free radicals away, protects against the exposure to toxic substances, inflammation, or allergies that amount to deteriorated brain performance. This is one particular reason why the diet lowers the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Many studies have linked diet with Alzheimer’s disease. From a systematic review published in 2013, it was found that diet, the disease, and cognitive decline had a correlation. Another review conducted in the same year arrived at the same results, but it additionally realized a negative association with the potential of the progress from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. However, it acknowledged that studies covering the topic are only a handful.
Another clinical research published in 2016 linked the Mediterranean diet with improved cognitive ability. However, the only quibble from the study is that there was no conclusive indication as to whether the relationship between the two is causal.
The ingestion of foods like kefir, yogurt, and other probiotic foods, which are healthy for the digestive system, has also been proven to improve someone’s mood, foster brain functionality, and improve memory.
What if you could make small changes to your diet that lead to lifelong changes in weight and overall health? Noom is based on clinical and psychological evidence to help you stick with your new eating habits.
Noom just works – give it a try.
Helps You Live Longer
Cited as the number one healthy diet, the Mediterranean type of eating is certainly winning as the best combination for leading a long life. In a nutshell, it prevents early deaths from several diseases and factors related to brain function and cardiovascular diseases, as evidenced by the numerous studies and the Mediterranean diet benefits.
Some of the leading causes of deaths in the United States and some other parts of the world are depression, heart disease, diabetes, cognitive decline, inflammatory diseases, and Alzheimer’s disease, to name a few.
The famous Lyon Diet Heart Study is a perfect testimony on how the diet helps you improve your health. It affirmed that the diet lowers the risk of all-cause death by 45 percent compared to other diets. The findings indicated that the Mediterranean style of meal plans is ideal for lowering the risk of heart disease by 70 percent. This value is close to three times the reduction potential realized by a majority of the cholesterol-lowering prescription drugs.
Although the diet lowers the level of LDL cholesterol, the study hinted that heart disease is about more than just cholesterol. There was no significant change in the levels of cholesterol. The benefits of the diet depicted by the study were groundbreaking, and it has since been a topic of review.

Helps You Relax and Lead a Stress-Free Life
As earlier mentioned, the diet is more of a lifestyle than a structured plan. It gives one a chance to interact with nature, harvest local produce, or visit farmers and their farms. This allows you to spend sufficient time in nature, acquire good sleep during the night while fostering good bonding with the family.
Moreover, the Mediterranean food list is rich in ingredients with probiotics and prebiotics, which are good for improving your mood, helping you to relax and stay calm. This same benefit can also be derived from the diet’s positive influence on brain function.
As exercise is part of the Mediterranean healthy living diet, indulging yourself in workouts, eating healthy every mealtime, and dining at your own pace and comfort helps in the maintenance of a happy mood.
The fascination of the Mediterranean eating plan includes a love for red wine. Not only is the diet ideal for aging gracefully, but it is also advantageous and beneficial in the fight against overweight issues, among others. It also fosters the baying of complications, hormonal imbalances, weight gain, inflammation, and fatigue.
Food on the Mediterranean Diet
Mediterranean Diet, Bread, and Grains
Copious amounts of pasta, grains, or bread in a Mediterranean diet are not necessary. Even though vegetables make the predominant food, experimenting with whole grains is part of the plan. There are many types of grains to choose from. The first thing to do is to kick the refined grains to the curb. To maximize health benefits, the focus should be on whole grains, which contain low levels of unhealthy fats.
Bulgur, a grain with origins in the Middle East, comes with enough antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties to be beneficial to health. Farro is another exemplary alternative with minerals such as zinc and iron. It also contains fiber and B vitamins.
Whole oats, whole-wheat pasta, couscous, rye, and whole-grain bread are other types of ingredients you should include in your diet. Whole-grain breads are pivotal in the diet. However, the bread shouldn’t be eaten with margarine or butter, or jam for that matter. Instead, dip it in olive oil or eat it plain. If you can’t get the 100% whole-grain bread, you can easily bake your own. You can also use other varieties of wheat like Kamut and spelt.
Mediterranean Diet and Nuts
Nuts contribute to the principles that guide the Mediterranean diet. They are plant-based, sweet, and a dependable source of unsaturated fat, which is good for the health of your heart.
There is a broad range of these food types to choose from. They include:
Almonds
Have a handful of almonds. They are tasty, nutritious, and are following the dietary guidelines of this diet. You can have the almonds whole or by incorporating them into your daily recipes. Dip an almond in olive oil and munch it. Toss or mix almonds in salads, spices, or herbs as a healthy snack! The options are almost limitless. You can chop them into a bowl of whole grains like steel-cut oats or combine the nuts with sliced onions, minced garlic, and garnish with olive oil for a nourishing addition to your grilled fish.
Walnuts
These nuts contain healthy fatty acids – omega-3 – which makes them highly nutritious if incorporated into a diet. You can stir them in low-fat Greek yogurt or eat them plain. You can also experiment with walnuts in a variety of recipes to see what works best for you.
Hazelnuts
Apart from being rich in B vitamins, hazelnuts come with flavonoids like proanthocyanidins – the same form of antioxidants in green tea that gives it remarkable health benefits. You can eat them raw, roasted, or ground and mixed with flour for baking bread.
More Nuts
The majority of the nuts are ideal for a healthy eating habit. Apart from the above three types of nuts, there are other delicious nuts, including the pignoli or pine nuts, pecans, pistachios, macadamia, cashews, and some seeds can be blended into sauces, yogurt, salads or consumed whole as snacks.
The nuts should, however, be consumed in moderation if your goal is to use the Mediterranean diet to lose weight. Some of them are high in calories, and it is recommended that one has only a handful a day. Similarly, heavily salted, candied, or honey-roasted nuts should be avoided.
Never have to worry about avoiding foods again. You can eat the foods you love and still lose weight and keep it off.
Take Noom for a spin to see what it feels like knowing you’re losing weight for the last time.
Mediterranean Diet, Processed Foods, and Sweets
Some foods are not recommended on a Mediterranean diet. While it doesn’t cut them off entirely excluding them from the menu, it uses them sparingly. Processed foods have a bad rap. They are a major cause of vascular disease and weight-loss problems. Limiting these foods in your plan is a healthy choice.
Reduce the intake of red meat, be it lamb, beef, or pork. These meats should be consumed moderately. Red meat is high in saturated fats and trans fat, which may result in irreparable damage to the body.
Processed foods are also laden with salt and, in some cases, saturated fats. In contrast, others have no nutritional value, most of them are loaded with calories that contribute to uncontrolled weight gain. In addition to processed foods, excluding sweets or foods with too much sugar is a step in a positive direction. Refined grains and margarine, for example, are sweet, but they contain unhealthy fats.
Sugar-sweetened beverages, added sugars, processed meat, refined grains, refined oils, and any other highly-processed food shouldn’t make the frequent recipe list. The secret is to stick to fresh foods instead.
Trans Fats Vs. Saturated Fats
Studies suggest that the best fats to choose are unsaturated fats, but as it turns out, one doesn’t need to eliminate all fats from the body. Substituting them with healthier types is recommended.
Fat is essential for your health. It anchors several body functions. For example, some vitamins cannot be dissolved without fat. That means they cannot be used by the body in the absence of some fats.
Some fats are high in calories, and if you eat more than you require, weight gain abounds. As a result, poor health and risk of cardiac diseases arise. The two potentially harmful fats are:
Trans Fats
It is perhaps the worst type of fat that is a byproduct of the hydrogenation process – a procedure that solidifies healthy oils. Hydrogenation also prevents the oils from becoming rancid. This type of fat is often indicated as “partially hydrogenated oil” on the food label.
Initially, trans fats were mainly found in vegetable shortenings or margarine (solid). But the rise of the food manufacturing industries saw the beginning of trans fats in most processed foods even in pastries and French fries.
Trans fats possess no known health benefits, and an optimum level of consumption is hard to draw. Elevated consumption of these types of fats decreases the amount of good HDL cholesterol while promoting oxidized low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol. The fats lead to inflammation associated with cardiac diseases and insulin resistance.
Saturated Fats
These are the in-between fats in the American diet. At room temperature, they have a solid-state. The name “saturated” comes from the distinguishing characteristic. Each carbon atom holds as many hydrogen atoms as possible. The fat is saturated hydrogen.
Saturated fats aren’t as bad as trans fats, but in large quantities, could be detrimental to a person’s health. However, it is unclear whether the fat falls under the bad or the good. On the one hand, research suggests that high consumption of saturated fats may lead to heart disease, diabetes, and even stroke.
A diet full of saturated fats elevates the total cholesterol bringing imbalance between HDL and LDL cholesterol. Too much of the bad cholesterol causes the vasoconstriction of the arteries due to deposition of fats that make them narrow. This forces the heart to work harder to pump blood across the body, hence the risk of heart disease.
On the other hand, recent studies have failed to establish a link between saturated fats and the risk of cardiovascular disease. A meta-analysis examining the other 21 clinical studies claimed that there wasn’t sufficient evidence to prove that saturated fats cause heart disease. However, it found out that replacing the fats with the polyunsaturated types goes a long way in reducing the risk.
Two other studies also reaffirmed the claim by narrowing them down a bit. That is, they concluded that the replacement of saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats such as vegetable oils or the consumption of high-fiber carbs is ideal for reducing the risks of cardiac problems, but the opposite could happen if one replaces the fats with highly processed carbs.
That said, saturated fats are contained in most junk and other processed foods, including red meat, whole milk, and other related products, manufactured or commercially made or baked goods like cookies, coconut oil, and many other food sources.
Monounsaturated Vs. Polyunsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats are considered healthy or good fats. They have fewer bonds of hydrogen, and they have a liquid form at room temperature. Several organizations, including the American Heart Association (AHA), urge people to use these types of fats or consume enough foods containing them. The Mediterranean diet uses olive oil as the primary source of fat. Olive oil, which contains linolenic acid, is one source of unsaturated fats. Other sources of these types of fats include fish, vegetables, seeds, and nuts.
There are two broad categories of unsaturated fats. They are:
Monounsaturated Fats
Olive oil is a perfect example of monounsaturated fats. Whenever you dip that nut into olive oil or when you garnish your salad with it, you are consuming one of the healthiest fats. Unlike saturated fats, monounsaturated fats have only a single pair of carbon molecules linked together by a double bond, meaning it has fewer hydrogen atoms. Sunflower oil, high-oleic safflower, the majority of the nuts, avocados, canola oil, and peanut oil are other sources of monounsaturated fats.
The discovery of the benefits of this fat arose from the Seven Countries Study when it was linked with lower mortality rates resulting from heart diseases. The people from the region of the study didn’t source their fats from animals. Instead, olive oil was the predominant type of fat they consumed.
There is no recommended daily intake of monounsaturated fats. Experts and the Institute of Medicine recommend that you use as much as you can in tandem with the other type of good fats – polyunsaturated fats. Include the mentioned types of oils and seeds in your diet as substitutes for margarine, butter, or lard as you cook. Nuts being good sources of unsaturated fats should be consumed in moderation at least once a day.
Healthy fats are a critical part of any successful health, wellness, and weight-loss program.
Check out Noom to see how these healthy fats fit into your meal plan.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats are essential for the body’s optimal function. Even so, the body cannot make them, and the only source is from the foods you consume. Their function is to construct the cell membranes apart from covering the nerves. The fat is also beneficial for blood clotting, inflammation, and the movement of muscles. Unlike the monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats have two or more pairs of carbon linked with double bonds.
Polyunsaturated fats are further divided into two; the omega-3 fatty acids and the omega-6 fatty acids. The numbers in these fatty acids define the distance of the carbon chain and its first double bond. The two types of polyunsaturated fats offer beneficial effects to a person’s health.
Foods containing polyunsaturated fats include corn oils, safflower oil, fish – sardines, salmon, and mackerel – unhydrogenated soybean oil, sunflower oil, some nuts such as walnuts, flaxseeds as well as canola oil.
As the body needs fat for energy, consuming enough healthy fats is the way to go. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, you should get at least 25 to 30 percent of the number of calories you consume from fats, specifically monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats. This means that you should switch from saturated fats to the good fats or simply have enough Mediterranean food recipes daily.
Benefits of Unsaturated Fats
Both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats have remarkable health benefits. They both help lower the levels of cholesterol, keeping your heart healthy, and numerous studies are supporting this claim. The fats regulate blood sugar and insulin levels, which helps in the overall health, but especially advantageous for the diabetic.
The polyunsaturated fats are beneficial for the reduction of blood pressure, irregular or elevated heartbeats, and slows the deposition of plaque in the arteries.
The Mediterranean Diet and Omega 3 Fatty Acids
The Mediterranean diet follows a diet of food sources rich in fatty acids. Fish, as already mentioned, contain omega-3 fatty acids – a type of good fats. Fatty fish such as mackerel, lake trout, herring, sardines, albacore tuna, and salmon are rich sources of fatty acids.
The health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids range from improved brain function, the immune system, and better cognitive ability. There are also numerous studies supporting the fact that the fatty acids lower the triglyceride levels and stabilizing the blood pressure, which protects against potentially lethal heart problems.
The omega-3 fats are also ideal for fighting inflammation, decreasing liver fat, and reducing weight as well as waist size.
The Mediterranean diet recommends that you eat fish once or twice a week regardless of whether it is fresh or water-packed. Include tuna, salmon, trout, mackerel, and herring in the diet and avoid fried fish! If you have to fry them, perhaps using a small amount of canola oil would be commendable, otherwise, have your fish grilled. You will get enough of the omega-3 acids if you follow this diet plan.
The American diet doesn’t contain enough omega fatty acids, unfortunately. Most Western diets contain most of the other types of polyunsaturated fat; the omega-6 fatty acids.
Even so, finding a balance between the two fatty acids is appropriate if the body is to reap all the health benefits. The right ratio is 4:1 (omega 3 to omega 6) not 10:1, and above like in many Western meal plans.
There is another type of fatty acid is called omega-9. It is monounsaturated fat, unlike the other two, and they make many of the fats contained in cells. This means they are non-essential as the body produces them. The omega-9 fatty acids are useful for metabolic health.

Have Your Wine and Drink it Too on the Mediterranean Diet
Along with eating any type of Mediterranean food on the allowed list, make a point of having a glass or two of wine in a day. According to the Mayo Clinic, alcohol, taken in moderation with an emphasis on red wine, is ideal in the diet. Many Mediterranean recipes include red or white wine as one of the ingredients of the food list.
Wines are fermented from the juice of various varieties of grapes. Like fruit juices, grapes also contain phytonutrients. The most common types of wine are the red and white wines, but there is another variation; the rose type. So, which one should make it to the Mediterranean food consumption?
What the Med diet pyramid suggests as a glass of wine is the red type. Although both the popular types of wine have phytonutrients, the white variety lacks some of the pivotal nutrients advantageous to the body because of the process used in its manufacture. However, red wine comes from whole grapes. It is rich in polyphenols containing flavonoids.
The wine is antioxidant-rich, a trait hailed for health benefits. It fights diseases through the inhibition of cellular oxidation. Red wine also keeps the oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in check as it boosts good cholesterol. Cumulatively, the effect is claimed to help prevent cardiac attacks. Moreover, the antioxidants in wine nourish the immune system, which in turn allows you to age gracefully while at the same time fighting other infections and diseases.
The diet recommends a moderate amount of wine of no more than five ounces daily for women or men over 65. Contrariwise, the recommendation for men under that age should be no more than 10 ounces daily.
We agree, you can drink your wine and lose weight too.
Noom works with whole foods and natural changes to help users lose those extra pounds for the last time. Success happens with Noom.
The debate on the benefits of alcohol is controversial, and choosing the right one might be overwhelming for some people. Vintage wines sometimes deteriorate their phytonutrients. As a result, you should consume young red wine. Try red wines from the Mediterranean region like southern Italy, Sicily, Greece, Sardinia, and southern France. These wines, together with those from high-altitude areas like Washington and several parts of Australia, are known to be rich in procyanidin – one of the antioxidants in wine.
To make things easy, Cabernet Sauvignon, Old Vine Zinfandel, Nebbiolo, Malbec, and Sangiovese are the few options you can look for.
Review of Mediterranean Diet Basics
Eat whole grains, vegetables, fruits, seafood, use herbs and spices, fish, seeds, potatoes, and don’t forget to include healthy oils such as olive oil.
Minimize the intake of yogurt, cheese, poultry, eggs, and other dairy products. Also, spare red meat for special occasions, swap with fish or poultry, or eat it in small portions.
Forget about highly refined or processed foods. Refined oils, grains, commercially-processed meat, and sugar-sweetened beverages.
Mediterranean Diet Foods to Avoid
The following foods are to be avoided on a Mediterranean diet as they are considered unhealthy.
Ice cream, chocolate, candies, table candies, sweets, soda, commercially made juices, and basically all the lists of added sugars.
Refined grains like white bread, bowls of wheat pasta, cereal, bagels, and many more.
Saturated and trans fats included in margarine, some animal fats, butter, and others.
Most of the refined oils like soybean, cottonseed, and vegetable oil. Stick to olive oil that contains linolenic acid, which is beneficial.
Red meat isn’t the only type of meat to avoid. Ensure that your easy Mediterranean diet recipes or bought ingredients do not include hot dogs, processed sausages, or bacon.
Highly-processed foods are generally a no-no in the diet. They all constitute the junky and unhealthy diet meals that have more negative effects than benefits. If it comes in a box, don’t eat it. The same goes for packaged foods labeled “low-fat” foods.
To effectively ensure that you don’t include these foods in your Mediterranean diet meals, read the label for the list of ingredients. This is particularly the case if you are relying on a Mediterranean diet shopping list as you go about.

Myths and Facts About the Mediterranean Diet
Here are some popular myths about the Mediterranean diet and their facts:
It Doesn’t Work Outside the Mediterranean Region and is Hard to Follow
Anyone can adapt to this type of diet plan by paying attention to specific healthy food types. Although some of the foods are specific to the Mediterranean climate, most of them can be easily found here.
Some farm produce grown in high altitudes and Northern America, for example, will fit the Mediterranean-style eating impeccably. Think about some of the wine and blueberries.
Consequently, the diet isn’t hard to follow. It simply is like following a regular healthy eating pattern. It might only be a little hard to stick to if you are not used to cooking at home or when you want to increase the consumption of certain foods while decreasing others.
It is Expensive
Eating healthy, akin to the Mediterranean diet, is too expensive, some people claim. However, if you are creating meals from plant-based, or natural sources, that is, if you are using legumes as your source of proteins, among other whole-food examples, the diet will eventually prove to be less expensive than dwelling on lots of processed foods.
Studies also show that the diet is not necessarily linked to the high costs of food products. The paper “The Mediterranean Diet: Does it have to cost more?” published in the 2009 issue of the Public Health and Nutrition Journal by Adam Drewnowski of the University of Washington’s Center for Obesity Research, shines a light on the myth. The observation was that for the avoidance of elevated costs of the overall dietary costs, consumers need to be educated on lower-cost food types. In contrast, they minimize the buying of expensive ones in large quantities.
Drinking Wine with Every Meal is Fine
The fact is, wine is used in moderation. The drink is sugary and too much – more than two or three glasses of wine – may deliver unpleasant results. Wine should be used in moderation. At least one glass a day for women, and two for the men.
The Mediterranean Diet is All About Pasta, Pizza, and Cheese
Although pasta is part of the diet, the Mediterranean-style cooking only applies about half a cup, or on some occasions, a full-cup serving. If the diet is about anything, then it all comes down to pulses and veggies garnished with olives! The rest of the dish mainly consists of vegetables, salads, fish, only a few pieces of grass-fed meat, and often a slice of bread.
Never be misled by racks of lamb, pizza, gyros, long loaves of bread, or commercially- produced foods labeled as appropriate for substitutes of the fresh foods in the Mediterranean diet. True, the foods make part of the diet, but it isn’t a whole bowl of plain pasta and a few additions like in the American diet.
It is Only About the Food
The diet isn’t only about food. That makes up a huge part of the diet, but the healthy eating lifestyle doesn’t include sitting in front of the TV while you are at it or doing it hastily. On the contrary, it is about taking time, relaxing, and sharing a meal with others.
Sharing food with family and friends fosters a deep appreciation for the fancies of savoring a delicious meal. Physical activity is also a must. The health benefits the people of the Mediterranean enjoy has been attributed, in part, to exercise. They traveled back and forth to get their food. This contributed to their overall health.
The Diet is Too High in Fat
Mediterranean diet replaces saturated fat types like vegetable oil and butter with healthy types like olive and coconut oil. It does away with the saturated fats that are contained in large amounts in the typical American diet.
The unsaturated fat types are recommended in people’s everyday eating, and there are research studies to support the fact. Experts agree that the type of fat consumed has a direct health impact on your body. Nuts, olive oil, fish, and some fat from cheese and Greek yogurt are good for overall health and wellness.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Cannot be Used to Cook
This isn’t an unfound claim considering olive oil loses its flavor when heated. Despite the loss of the unique flavor, olive oil doesn’t become unhealthy when used to cook food.
Unlike refined oils such as the vegetable, canola, and coconut oil, olive oil has a very low smoke point. The smoke point of the extra virgin olive oil depends on the age as well as its condition.
To prevent the oil from being damaged, the temperature range for good quality olive oil is 350 to 410 degrees Fahrenheit. If your fat has gone rancid, that means you probably have a lower-quality product.
The Mediterranean diet dates to more than four thousand years ago. As such, one can safely say that it is the oldest diet in the world! Nonetheless, the introduction to other parts of the world, particularly the western countries like the United States was realized barely seven decades ago. Thanks to the nutritionist and professor from the University of Minnesota, Ancel Keys, who did the rediscovery and sparked a perpetual series of studies and the spread of the Mediterranean diet.
A diet rich in nutrients like the Mediterranean diet is an excellent way to eat better – eat healthier. Noom helps you find the best way for you to lose weight with personal coaches, extensive food databases, recipes, and more.
All you do is commit 10 minutes a day for success. Check out Noom today!
Questions and Answers (QA)
Q: What foods are not allowed on the Mediterranean diet?
A: There are no foods that “are not” allowed on the Mediterranean diet. Red meat should be consumed infrequently – as little as once a month.
Q: What foods can you eat on the Mediterranean diet?
A: Based on the Mediterranean diet food pyramid, your diet should include whole-grain bread and grains, fruits, beans, seeds, nuts, vegetables, olive oil, cheese, yogurt, and various forms of lean proteins.
Q: What do you eat for breakfast on the Mediterranean diet?
A: A common breakfast on the Mediterranean diet could include a serving of yogurt, a slice of whole-grain toast, and a scrambled egg.
Q: Why is the Mediterranean diet so healthy?
A: Though difficult to pinpoint one reason why the Mediterranean diet is so healthy, it would likely be the anti-inflammatory properties. Various disease processes activate inflammation, including obesity. Reducing that inflammation can reduce the effects on your health.
Q: Is peanut butter OK on a Mediterranean diet?
A: Yes, it is suggested, based on the Mediterranean diet food pyramid, to eat nuts and seeds daily. Natural peanut butter fits perfectly into the diet.
Q: Can you eat pizza on a Mediterranean diet?
A: Absolutely. You can eat pizza on a Mediterranean diet. With the popularity of cauliflower crusts, it’s easier than ever to add pizza to your diet.
Q: Is bacon on the Mediterranean diet?
A: No food is expressly forbidden on the Mediterranean diet. You can eat bacon, but eat in moderation at bacon is high in fat.
Q: Is the Mediterranean diet anti-inflammatory?
A: By nature, due to the concentration on healthy fat intake, like olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish, the Mediterranean diet does have anti-inflammatory properties.
Q: Is the Mediterranean diet low carb?
A: The traditional Mediterranean diet is not low carb, but you can follow a low-carb diet inspired by the foods commonly eaten in the Mediterranean like fatty fish and fresh berries.
Q: Can you eat chocolate on the Mediterranean diet?
A: Yes, dark chocolate is encouraged, in moderation, on the Mediterranean diet.